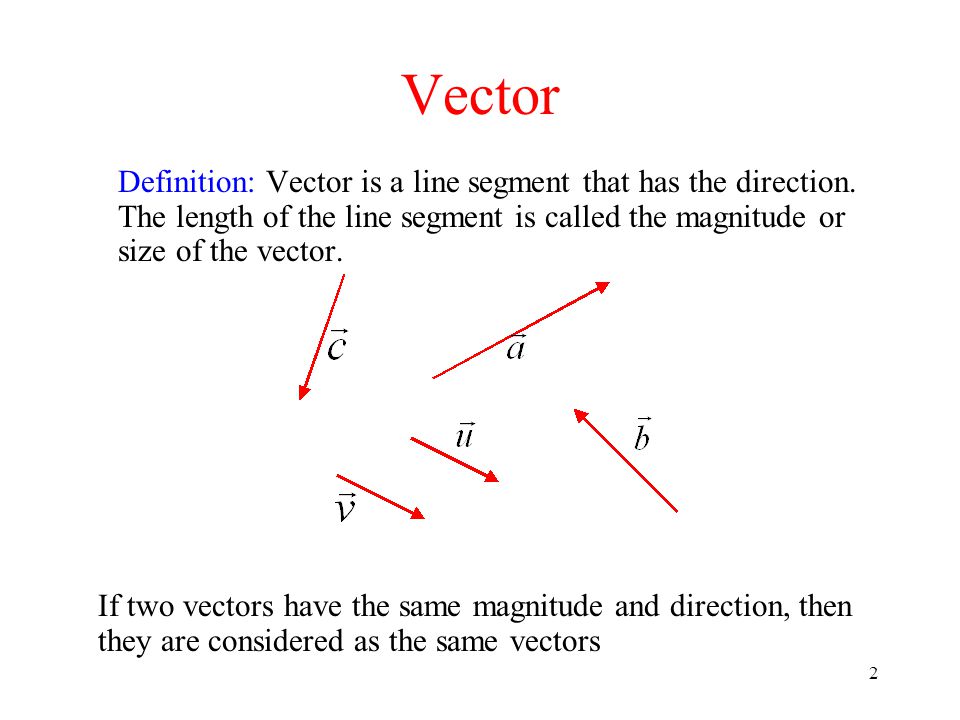
Definition Of A Vector In Math . The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. A vector is a directed line segment. It is used to represent physical quantities like. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). definition 51 vector. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. definition of a vector. vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction.
from www.vrogue.co
A vector is a directed line segment. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: definition of a vector. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction.
What Is Vectors vrogue.co
Definition Of A Vector In Math The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: It is used to represent physical quantities like. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. definition 51 vector. definition of a vector. A vector is a directed line segment. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction.
From printablelibraryharley.z21.web.core.windows.net
Physics Classroom Vector Addition Definition Of A Vector In Math definition of a vector. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). Vectors are. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From thirdspacelearning.com
Translation GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet Definition Of A Vector In Math A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. It is used to represent physical quantities like. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. A vector is an object. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.youtube.com
Vectors (Part1) Definition & Graphical Representation, IITJEE Definition Of A Vector In Math definition 51 vector. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. Given points. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From math.stackexchange.com
linear algebra Column vectors as entries of a column vector Definition Of A Vector In Math vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction.. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From vectorified.com
What Is A Column Vector at Collection of What Is A Definition Of A Vector In Math Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: definition of a vector. The length of the line shows. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From study.com
What is a Vector? Vector Magnitude, Components & Examples Lesson Definition Of A Vector In Math vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. definition 51 vector. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). A vector is an object. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.cuemath.com
Unit Vector Formula, Definition, Caculate, Notation Definition Of A Vector In Math in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: definition of a vector. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. A vector is an. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.pinterest.co.uk
Vectors Physics and mathematics, Physics formulas, Physics notes Definition Of A Vector In Math A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). It is used to represent physical quantities like. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From robertvandeneynde.be
Mathématiques Trigonométrie, vecteurs et matrices Definition Of A Vector In Math vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction.. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.biologyonline.com
Vector Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Definition Of A Vector In Math Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction. A vector is a directed line segment. It is used to represent physical quantities like. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). A vector is an object that has both a magnitude. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.pinterest.com
Vector Problems with Ratio Students learn how to solve problems with Definition Of A Vector In Math Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. A vector is a directed line segment. definition of a vector. vectors, specifically euclidean vectors, are mathematical objects that encode magnitude and direction. It is used to represent physical quantities like. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.teachoo.com
Find the projection of the vector a = 2i + 3j + 2k on vector b=i+2j+k Definition Of A Vector In Math Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. A vector is. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.kristakingmath.com
Using translation vectors to transform figures — Krista King Math Definition Of A Vector In Math definition 51 vector. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. definition of a vector. A vector is a directed line segment. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. A vector is an object that has both a. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.youtube.com
Introduction of vector algebra definition of vector class 12 Definition Of A Vector In Math The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. It is used to represent physical quantities like. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. definition 51 vector. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. vector,. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From brilliant.org
Vectors Brilliant Math & Science Wiki Definition Of A Vector In Math definition of a vector. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. It is used to represent physical quantities like. vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment,. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. A. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.vrogue.co
What Is Vectors vrogue.co Definition Of A Vector In Math vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: definition of a vector. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. definition 51 vector. in maths, vectors are objects that have. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.teachoo.com
Example 3 In Fig, which vectors are (i) Collinear Type of vector Definition Of A Vector In Math The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. a vector is a mathematical entity that has magnitude as well as direction. in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. A vector is a directed line segment. Vectors are ubiquitous in physics and. vector, in mathematics,. Definition Of A Vector In Math.
From www.grc.nasa.gov
Vector Addition Definition Of A Vector In Math It is used to represent physical quantities like. A vector has magnitude (size) and direction: definition of a vector. Given points \(p\) and \(q\) (either in the plane or in space), we denote with \(\vec{pq}\). in maths, vectors are objects that have both magnitudes as well as directions. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line. Definition Of A Vector In Math.